B2B payments: What to expect in 2024
Published: December, 12th 2023

The accelerated transformation in B2B payments seen in the last three years is set to continue into 2024 and beyond. As businesses look for more efficient ways to make and take payments and even fund their operations and growth initiatives, digital B2B payment technology is proving to be an effective solution.
While some companies were early adopters, digitising and automating their payment systems before the challenges of COVID-19, some players are yet to implement the tools that would address many common business cash flow and payment problems. Below, we outline some key statistics to give you an overview of the B2B payments market, both globally and in Australia. We also provide some insights into what trends are likely to emerge in B2B payments in the next year.
The state of the B2B payments market
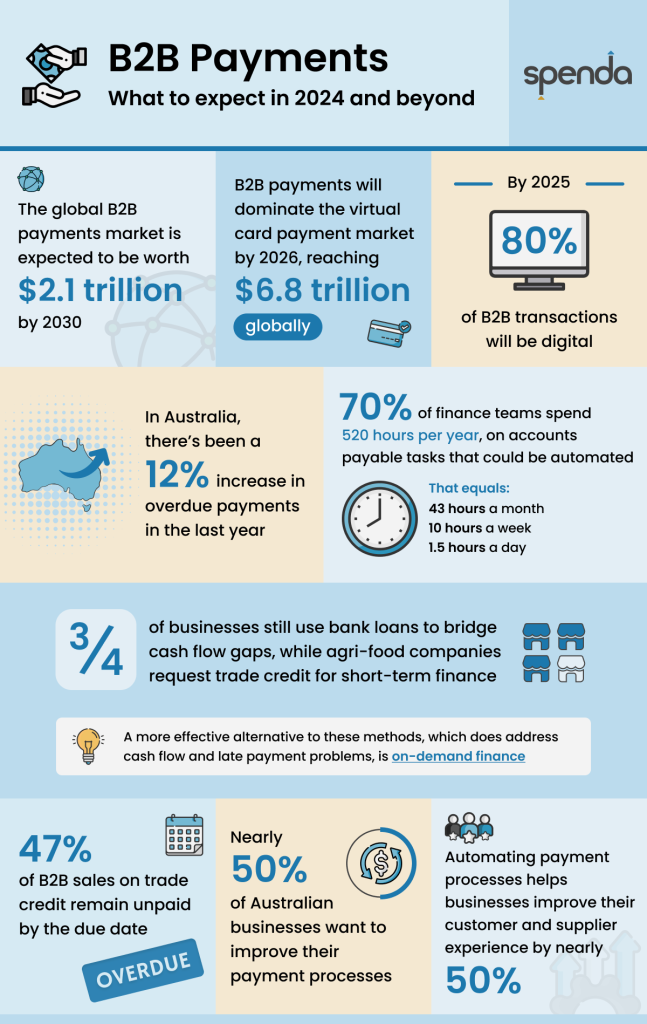
1. The B2B payments market continues to grow, forecasted at a CAGR of 10% through 2030.
The global B2B payments market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.1% through to 2030, making the market worth $2.1 trillion.
2. By 2025, most B2B transactions will be digital.
Digitisation has swept through B2B payments, particularly in the last three years. According to Gartner’s Future of Sales 2025 Report, 80% of transactions between suppliers and buyers will be digital by 2025.
Businesses that act now to get digital B2B payment systems and processes in place will reap the rewards now and into the future. Not only will these businesses save time, but they’ll also gather data that can be used to drive stronger commercial decision-making.
3. B2B payments will dominate the virtual card payment market by 2026.
By 2026, virtual card transactions will reach $6.8 trillion globally. With conveniences such as employee-issued cards and spend tracking, companies are embracing virtual cards, especially in remote workforces, to streamline and better manage spending.
4. Despite rising interest rates and lengthy approval processes, Australian businesses still rely on banks for some of their funding.
Three-quarters of businesses (75%) use bank loans to bridge cashflow gaps, while agri-food companies request trade credit for short-term finance. Other methods used to address cash flow issues amongst Australian businesses include delaying payments to suppliers and spending extra time chasing late payments. A more effective alternative to these methods, which does address cash flow and late payment problems, is on-demand finance.
5. Almost half of Australian businesses want to improve their payment processes.
46% of businesses now accept four or more payment methods. The most common methods include bank transfer, corporate credit card, direct debit, and digital payments. Despite offering a range of payment methods, 45% of companies say they need to improve their payment systems, with 40% discussing investment in changes at the executive or board level.
6. In Australia, there’s been a 12% increase in overdue payments in the last year, and 47% of B2B sales on trade credit remain unpaid by the due date.
When interest rates rise and high inflation persists, continuing to offer trade credit can be increasingly risky. For example, insolvency issues are a key cause of late payments in the agribusiness sector, rising to 7% of all outstanding invoices. To address these issues, solutions that extend payment times without the supplier carrying the risk are key.
7. Payment times from big businesses to SMEs in Australia remain unchanged despite policy developments aimed at reducing payment times.
Despite the Payment Times Reporting Scheme being introduced in January 2020, SMEs still wait an average of 32 days to get paid and up to 47 days in some cases. If you’re an SME that supplies products and services to large companies, taking control of your cash flow is more effective with third-party lending.
8. Automating payment processes delivers a better customer and supplier experience.
Forward-looking finance teams who have already automated their processes are reaping the benefits, with almost half (47 per cent) improving their customer experience and over 40 per cent providing a better supplier experience.
9. Most finance teams (70% of them) still spend 10 hours per week, or 520 per year, on accounts payable (AP) tasks that could be automated.
While 75% of Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) say they could complete processes and be fully functional while working remotely throughout COVID-19, many still haven’t automated tasks. Key tasks that AP teams still don’t automate include invoice processing, supplier inquiries, supplier payment execution, purchase order matching, new supplier registration, and payment reconciliation.
10. Almost 40% of accountants spend half their time on manual tasks.
Not only does automation cause errors and inefficiencies, but 39% of accounting professionals spend over half their time on manual tasks. And 42% of accountants who have been in the industry for more than 15 years found these manual tasks to be one of the most painful parts of the profession when they joined the industry.
Implementing solutions that automate accounts payable and accounts receivable processes not only saves time but can also improve employee engagement, particularly in finance and accounting teams.
Digitisation and point-of-sale lending will drive B2B payments in 2024 and beyond
Throughout 2024, expect to see a larger share of global B2B payments continuing to become digital. Along with this move, on-demand finance options that allow both suppliers and customers to collaborate on every transaction will boost cash flow across the supply chain. As these transactions flow into businesses, accounts payable and accounts receivable automation solutions will eliminate repetitive manual tasks, with AI-driven tools making it easier to reconcile transactions and complete reporting.
Of course, as more B2B payments move online, fraud can become more common. Taking measures to prevent fraud and ensure payment gateways are secure will be a top priority for companies moving into 2024. One way of making sure your payment solution has the highest standards of security is by finding the right payment facilitator (PayFac) partner for your business. A PayFac can look after all of the regulatory and administrative burdens of processing payments while ensuring you have the infrastructure to meet mandatory compliance regulations, which has varying levels based on your transaction volume.
Fund your business growth with Spenda
The shift to digital B2B payments and the ability to automate repetitive manual tasks can transform how businesses transact while making finance and accounting teams more efficient and strategic. With the right integrated payments provider, such as Spenda, businesses can boost their cash flow, stop the late payments problem at its core, strengthen their relationships with customers and suppliers, and access the capital they need to grow. If you want to hit the ground running in 2024, start by digitising your B2B payment processes and getting access to and offering on-demand finance.
Spenda serves as both a technology solutions provider and a payment processor, delivering the essential infrastructure to streamline business processes before, during, and after payment events. Our comprehensive solution empowers businesses to effortlessly manage invoices, facilitate payments, and even access on-demand funding, all within the Spenda ecosystem. With our integrated platform, businesses can optimise their financial operations and enhance overall efficiency.
